Anti-HA Tag Antibody (Mouse Monoclonal)
| CAT.NO | UNIT |
|---|---|
| G036 | 100 μg |
| Description | Hemagglutinin is an antigenic glycoprotein found on the surface of the influenza viruses, as well as many other bacteria and viruses. It is responsible for binding the virus to the cell that is being infected. The name hemagglutinin comes from the protein's ability to cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to agglutinate in vitro. |
|---|---|
| SKU | G036 |
| Unit quantity | 100 μg |
| Clone | HA.C5 |
| Raised in | Mouse |
| Clonality | Tag |
| Isotype | IgG3 |
| Species Reactivity | Other |
| Specificity | HA-tag monoclonal antibody. Recognizes HA-tagged tagged proteins overpressed in cells, including both amino- or carboxy-termini of targeted proteins in transfected mammalian cells. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide from influenza hemagglutinin epitope (YPYDVPDYA) coupled to KLH. |
| Applications | ICC/IHC/IF/IP 1:200 dilution. WB 1:1000 dilution. |
| Recommended Dilutions | ICC/IHC/IF/IP 1:200 dilution. WB 1:1000 dilution. |
| Formulation | Liquid |
| Concentration | 100ug/100ul |
| Storage Condition | This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. For extended storage, aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Expiration date is one (1) year from date of receipt. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH 7.4 with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Cellular Localization | Apical Cell Membrane |
| Guarantee | abm guarantees that all our Anti-HA Tag Antibody (Mouse Monoclonal) will perform as described on this product webpage, if this is not the case we will provide you with a one-time replacement at no extra cost. Documentation and explanation of experiment conducted will be required when submitting a claim for replacement. |
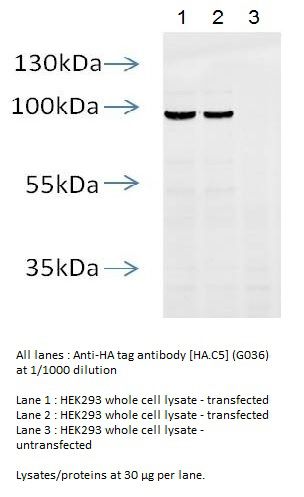
What dilution was used to achieve the WB and IF labeling pictured? What is the recommended dilution range for immunofluorescence?
The recommended dilution range for immunofluorescence for G036 is to use at an assay dependent dilution. The dilution for the labeled picture is 1:500.
What is the purification method for the tag antibodies?
We use Protein A affinity beads for all tag antibody purification.
What is the recommended dilution range for Western Blot?
We recommend to start with 1:1000 but the researcher should then optimized if needed for their experiments.
What is the size of the HA tag?
The immunogen sequence for the HA tag is YPYDVPDYA, which is about 1.1 kDa.
What is the dilution recommended for immunoprecipitation?
This product is provided with a recommended starting dilution for WB only. It is not yet tested in other applications such as IP, therefore optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Armistead, J et al. "Mutation of a Gene Essential for Ribosome Biogenesis, EMG1, Causes Bowen-Conradi Syndrome" Am J Hum Genet 84 (6):728-739 (2009). DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.04.017. Application: Immunoblot.
- Irie, T et al. "Significance of the YLDL motif in the M protein and Alix/AIP1 for Sendai virus budding in the context of virus infection" Virology 405 (2):334-341 (2013). DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.06.031. PubMed: 20605035. Application: Western Blot.
- Li, P et al. "Multiple roles of the candidate oncogene ZNF217 in ovarian epithelial neoplastic progression" Int J Cancer 120 (9):1863-1873 (2007). PubMed: 17266044. Application: Western Blot.
- Escamilla-Powers, JR et al. "The tumor suppressor protein HBP1 is a novel c-myc-binding protein that negatively regulates c-myc transcriptional activity." J Biol Chem 285 (7):4847-4858 (2010). DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074856. Application: Immunoprecipitation.
- Green, JL et al. "The C. elegans ROR receptor tyrosine kinase, CAM-1, non-autonomously inhibits the Wnt pathway" Development 124 (22):4053-4062 (2007). PubMed: 17942487. Application: Immunoblotting.
- Bronnimann, MP et al. "A transmembrane domain and GxxxG motifs within L2 are essential for papillomavirus infection" J Virol 87 (1):464-473 (2013). DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01539-12. Application: Western Blot.
- Parker, JG et al. " The Contribution of NMDA Receptor Signaling in the Corticobasal Ganglia Reward Network to Appetitive Pavlovian Learning" J Neurosci 31 (31):11362-11369 (2011). DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2411-11.2011. Application: Immunostaining.
- Charbonneau, Me et al. "Autoprocessing of the Escherichia coli AIDA-I autotransporter: a new mechanism involving acidic residues in the junction region" J Biol Chem 284 (25):17340-17351 (2009). DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.010108. Application: Immunodection.
- Verpooten, D et al. "Control of TANK-binding kinase 1-mediated signlaing by the y134. 5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1." J Biol Chem 284 (2):1097-1105 (2009). DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805905200. Application: Immunoblot.
- Hayashi, A et al. "Pyripyropenes, fungal sesquiterpenes conjugated with α-pyrone and pyridine moieties, exhibits anti-angiogenic activity against human umbilical vein endothelial cells" Biol Pharm Bull 32 (7):1261-1205 (2009). PubMed: 19571395. Application: Western Blot.
- Daniel, CJ et al. "Detection of c-Myc protein-protein interactions and phosphorylation status by immunoprecipitation" Methods Mol Biol 1012:65-76 (2013). DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-429-6_5. PubMed: 24006058. Application: Immunoprecipitation.
- Leung, GP et al. "Rtt107 is required for recruitment of the SMC5/6 complex to DNA double strand breaks" J Biol Chem 286 (29):26250-7 (2011). PubMed: 21642432. Application: Immunoprecipitation.
- Jin, H et al. "A Herpesvirus Virulence Factor Inhibits Dendritic Cell Maturation through Protein Phosphatase 1 and IκB Kinas" J Virol 85 (7):3397-3407 (2011). DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02373-10. Application: Western Blot.
- Gong, R et al. "Bispecific engineered antibody domains (nanoantibodies) that interact noncompetitively with an HIV-1 neutralizing epitope and FcRn" PLoS ONE 7:e42288 (2012). PubMed: 22879932.
- Neilson, KM et al. "Specific domains of FoxD4, 5 activate and repress neural transcription factor genes to control the progression of immature neural ectoderm to differentiating neural plate" Dev. Biol. 365:363-75 (2012). PubMed: 22425621.
- Barr, DJ et al. "Clathrin-independent endocytosis of ErbB2 in geldanamycin-treated human breast cancer cells" J Cell Sci 121:3155-66 (2008). PubMed: 18765569.
- Harvey, MC et al. "Distinct effects of the mesenchymal dysplasia gene variant of murine Patched-1 protein on canonical and non-canonical Hedgehog signaling pathways" J. Biol. Chem. 289:10939-49 (2014). PubMed: 24570001.
- Prieto-Echagüe, V et al. "Regulation of Ack1 localization and activity by the amino-terminal SAM domain" BMC Biochem. 11:42 (2010). PubMed: 20979614.
- Cho, HJ et al. "EphrinB1 Interacts with CNK1 and Promotes Cell Migration through JNK Activation" J. Biol. Chem. : (2014). PubMed: 24825906.
- Lee, HS et al. "EphrinB1 controls cell-cell junctions through the Par polarity complex" Nat. Cell Biol. 10:979-86 (2008). PubMed: 18604196.
- Hwang, YS et al. "The Smurf ubiquitin ligases regulate tissue separation via antagonistic interactions with ephrinB1" Genes Dev. 27:491-503 (2013). PubMed: 23475958.
- Burston, HE et al. "Regulators of yeast endocytosis identified by systematic quantitative analysis" J. Cell Biol. 185:1097-110 (2009). PubMed: 19506040.
- Lee, HK et al. "Drought stress-induced Rma1H1, a RING membrane-anchor E3 ubiquitin ligase homolog, regulates aquaporin levels via ubiquitination in transgenic Arabidopsis plants" Plant Cell 21:622-41 (2009). PubMed: 19234086.
- Lee, JY et al. "Cell growth defect factor1, chaperone-like protein of POR1 plays a role in stabilization of light-dependent protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase in Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis" Plant Cell 25:3944-60 (2013). PubMed: 24151298.
- Su, B et al. "Adhesion-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling is controlled by the direct scaffolding of Src from FAK complexes to lipid rafts by SSeCKS, AKAP12" Oncogene 32:2016-26 (2013). PubMed: 22710722.
- Irie, T et al. "Inhibition of interferon regulatory factor 3 activation by paramyxovirus V protein" J. Virol. 86:7136-45 (2012). PubMed: 22532687.
- Ma, Y et al. "Inhibition of TANK binding kinase 1 by herpes simplex virus 1 facilitates productive infection" J. Virol. 86:2188-96 (2012). PubMed: 22171259. Application: Immunoblot.
- Ji, YJ et al. "EphrinB2 affects apical constriction in Xenopus embryos and is regulated by ADAM10 and flotillin-1" Nat Commun 5:3516 (2014). PubMed: 24662724.
- Dupé, A et al. "An Alba-domain protein contributes to the stage-regulated stability of amastin transcripts in Leishmania" Mol. Microbiol. 91:548-61 (2014). PubMed: 24620725.
- Liu, X et al. "Molecular and structural characterization of the SH3 domain of AHI-1 in regulation of cellular resistance of BCR-ABL(+) chronic myeloid leukemia cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors" Proteomics 12:2094-106 (2012). PubMed: 22623184.
- Son, J et al. "Pick1 modulates ephrinB1-induced junctional disassembly through an association with ephrinB3" Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1:659-667 (2014). PubMed: 24937449.
- Whittington, , N. et al. "Sox21 regulates the progression of neuronal differentiation in a dose-dependent manner" Developmental Biology 397 (2):237-247 (2014). PubMed: 25448693.
- Dupé, A et al. "Differential Subcellular Localization of Leishmania Alba-Domain Proteins throughout the Parasite Development" PLoS One 9:e0137243 (2015). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137243. PubMed: 26334886. Application: Immunofluorescence.
- Ko, K. Y., Lee, J. H., Jang, J. K., Jin, Y., Kang, H., & Kim, I. Y. "S-Glutathionylation of mouse selenoprotein W prevents oxidative stress-induced cell death by blocking the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond" Free Radical Biology and Medicine 141:362–371 (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.007.
- Lee, E., Lee, T. A., Kim, J. H., Park, A., Ra, E. A., Kang, S., ... & Lee, S. "CNBP acts as a key transcriptional regulator of sustained expression of interleukin-6" Nucleic acids research 45(6):3280-3296 (2017).
- Singh, R., Dangol, S., Chen, Y., Choi, J., Cho, Y. S., Lee, J. E., ... & Jwa, N. S. "Magnaporthe oryzae effector AVR-Pii helps to establish compatibility by inhibition of the rice NADP-malic enzyme resulting in disruption of oxidative burst and host innate immunity" Molecules and cells 39(5):426 (2016).


