CRISPR Stable Knockout Cell Line Generation
Trust abm to knock out your gene of interest in your chosen Human, Mouse, or Rat cell line using our CRISPR sgRNA lentiviral system. We have successfully completed many knockout projects in a variety of cell lines, including fibroblasts, blood cells, ovarian cells, hepatocytes, and many more. Just tell our dedicated and highly experienced team which gene to target, how your cells grow, and we’ll do the sgRNA design, cloning, lentiviral packaging, and stable cell line generation for you! For your experiment to evaluate the effects of the knockout, be sure to ask us to make a Wild Type Control Cell Line Expressing Cas9 for comparison in the same cellular lineage. Interested in a 100% Guaranteed Knockout service? Find out more here.
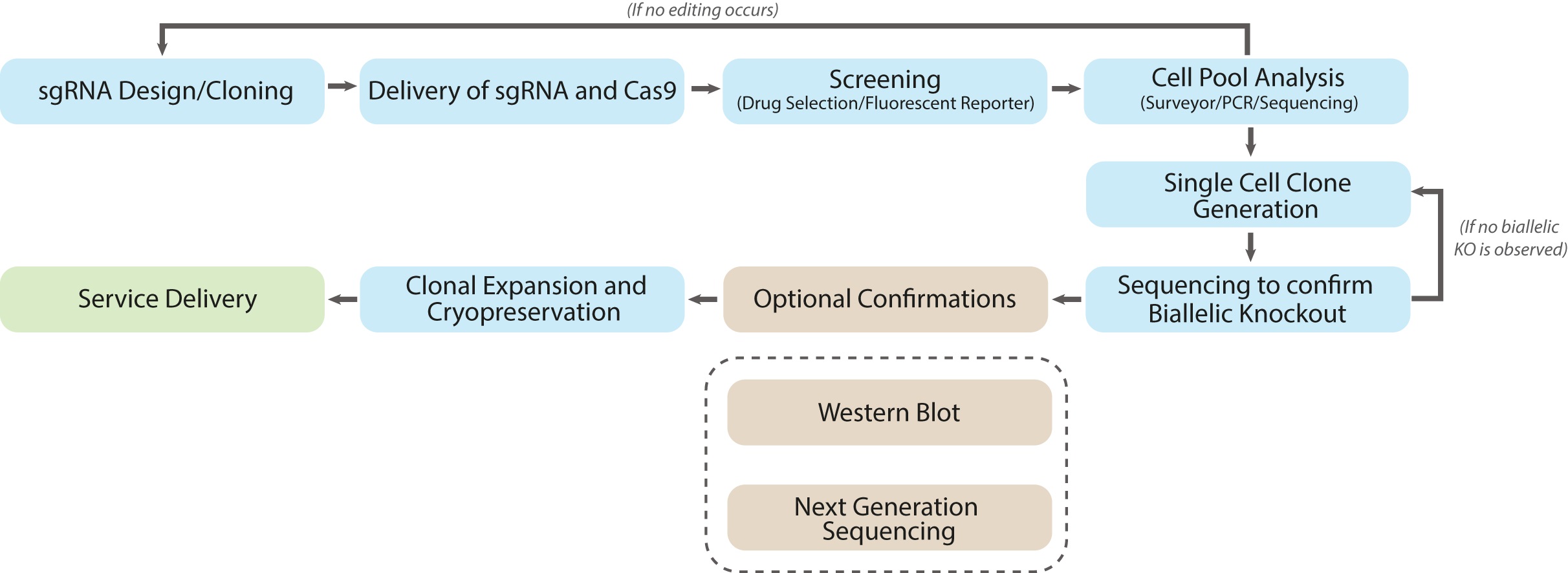
Workflow
Testimonial:
“We are quite happy with the knockout cells that you made. This was a tricky knockout and hemizygous removal was much more prevalent than the double knockout, but you did it. In addition to your excellent genomic sequence characterization of both mutant LIF alleles, I have confirmed in our lab that the tumor cells have lost all mouse LIF production.”
Dr. Robert Jackman, Boston University, Mouse LIF CRISPR Knock Out C26 Tumor Cell Line Generation and Screening Service, View case study here.
Additional Resources:
Service Details
abm provides RNA and DNA controls for quality control and validation of diagnostic tests.
| OUR BASIC PACKAGE (C208) INCLUDES | DELIVERABLES |
|---|---|
|
Sequence verified knockouts (at least 1 clone, 2 vials per clone)**, microbial/sterility tested with a service report. |
| ADD-ON SERVICES | UNIT | CAT.NO. |
|---|---|---|
| WT Control Cell Line Expressing Cas9 for Comparison (50% discount for academic customers if ordered with the basic package) | 1 Cell Line | C143 |
| Additional Clones^^^ | 1 Clone | C143 |
| Additional Vials of Delivered Cells^^^ | 1 Vial | C144 |
| Western Blot Validation Service (Up to 10 Clones Tested)## | 1 Service | C145 |
| Off-Target Analysis by Whole Genome Sequencing | Per Clone | C146 |
| Additional Rounds of Selection & Screening by Sanger Sequencing | 1 Screening | C147 |
| CRISPR-Cas9 Targeted Amplicon Sequencing | 1 Service | IA00100 |
| Cell Line Authentication: STR Profiling of 1 WT Parental Cell Line & 1 Knock-Out Cell Line Clone (50% discount if ordered with the basic package) | 1 Service | C287 |
Notes:
**Choose from HEK293, HEK293T, A549, HeLa, MDCK, A375, HepG2, HT1080 or U87MG. These cell lines are available as Cas-9 expressing versions or parental versions. Cas9 expressing version will be used by default. If the parental version is preferred, please request prior to order placement.
**The above pricing is valid for a single gene knockout for diploid loci only.
#Customer is required to provide at least 2 million cells, 1L of propagation media/any special coated flasks if needed (if cells need DMEM or RPMI, abm will supply media). Also, the cell line must tolerate single cell cloning and display adequate transfection and transduction efficiency.
##Pre-validated antibody needs to be provided by customer with appropriate positive control (preferably with supporting data).
^All add on services need to be indicated prior to order placement as the project design will need to be finalized prior to start of the service.
^^ Final Lead time may vary depending on actual growth rate of cell line while expanding from single cell.
Please note that if the gene to be knocked-out may be essential to cell survival, it is up to the end-user to proceed with the services. abm is unable to guarantee cell survival in these cases and will only attempt to rescue the clones under these conditions. abm is not accountable for cell survival if rescuing the clones (instructions to be provided customers) is unsuccessful.
^^^ Additional media or supplements may be required. For for-profit organizations and corporations, the price is 1.5 times the listing price.
Additional Info
CRISPR Stable KO Service Case Study
Using CRISPR to develop a biallelic LIF knockout in Mouse Colon Carcinoma Cells
- LIF locus in a Mouse Colon Carcinoma Cell Line, was knocked out using CRISPR targeted genome editing.
- Surveyor assay and sequencing results showed genome editing.
- After monoclonal selection biallelic knockout was confirmed by sequencing.
- abm will generate the desired stable cell line and perform QC.
Phase #1: Cas9 and sgRNA Delivery
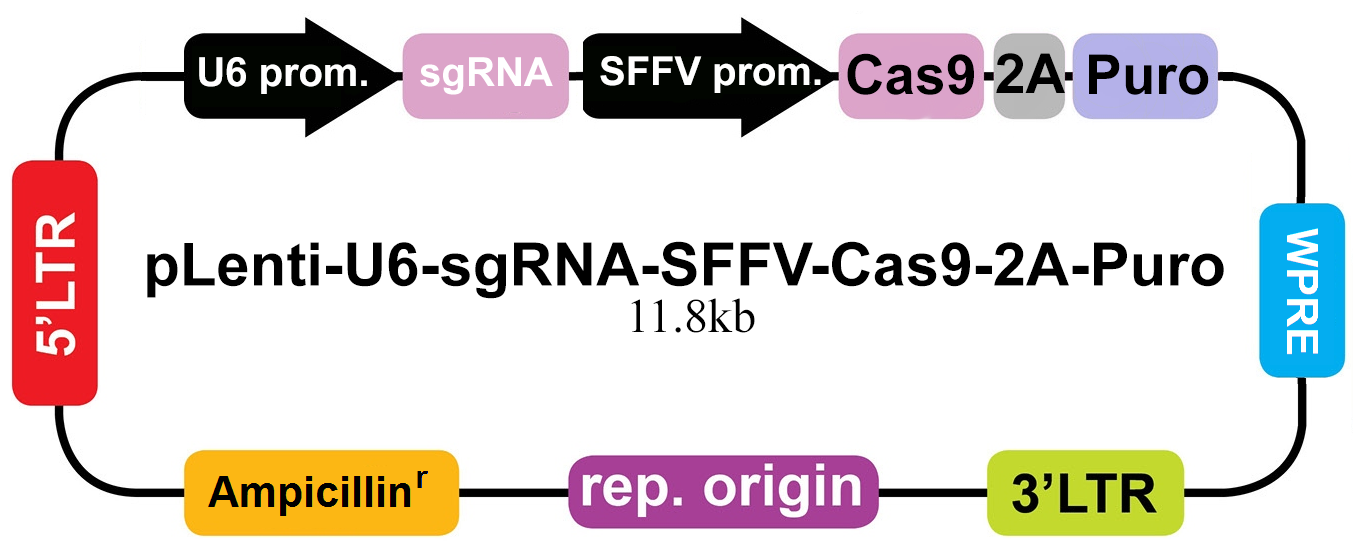
- Three sgRNA were designed against mouse LIF locus (Mus musculus, NM_008501). Software analysis was performed to ensure the sgRNA had no predicted off targets binding sites. The selected sgRNA design was then cloned into the pLenti-U6-sgRNA-SFFV-Cas9-2A-Puro All-in-One lentivector (Figure 1).
- Recombinant Lentiviruses were packaged using abm’s second generation Lentiviral packaging system. A multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5 was used to transduce the cells.
Phase #2: First Round of Colony Screening for Edited Clones
- Cell colonies are isolated after puromycin selection. Genomic DNA was extracted and the surveyor assay was performed to confirm genomic editing of the LIF locus.
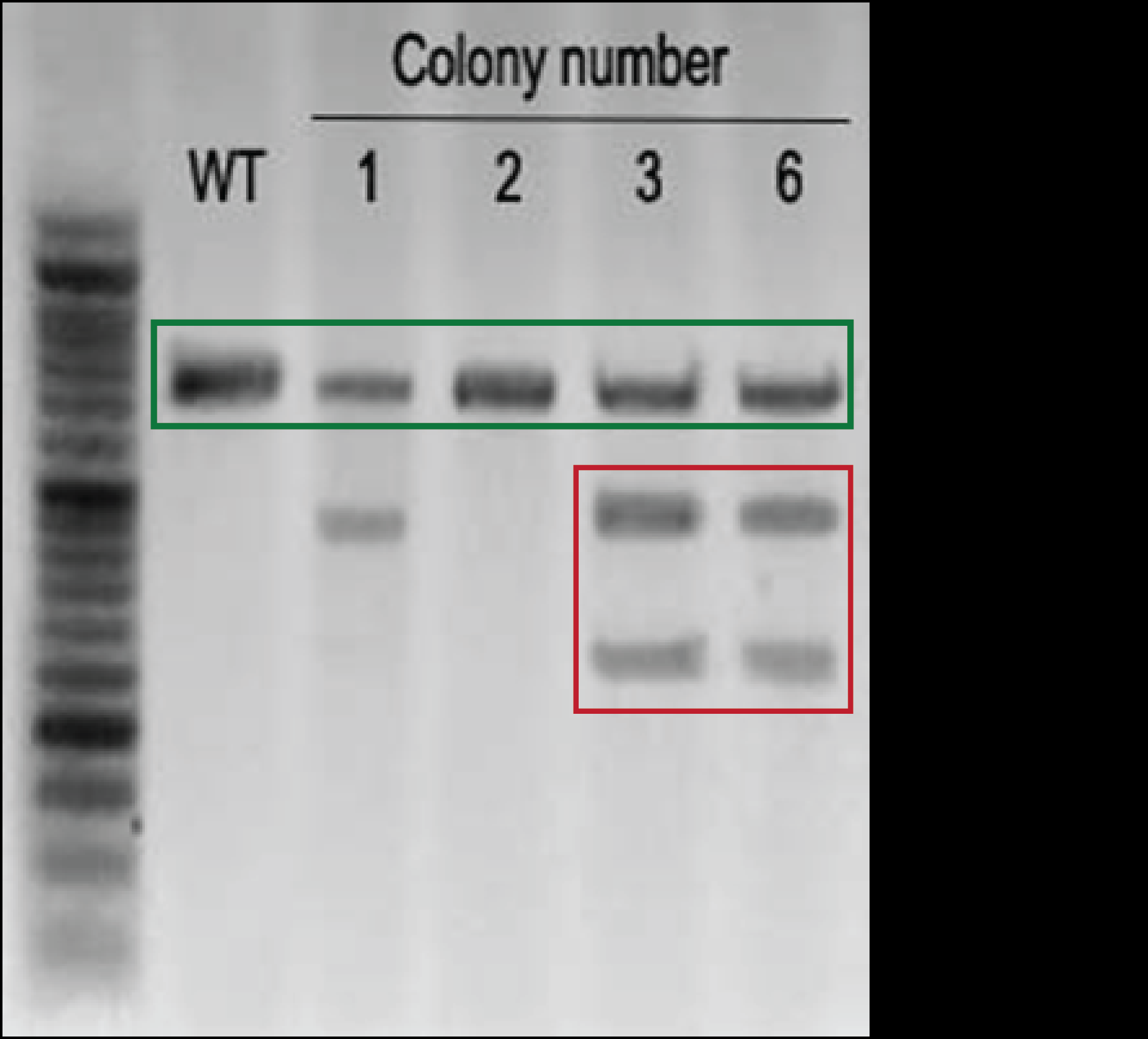
- A single band in a surveyor assay at the wild-type (WT) size indicates no editing has occurred; two smaller bands (that sum to the length of the WT) indicate editing has taken place.
- The surveyor assay (Figure 2) indicated that Colony 3 and 6 were edited; colony 2 was not edited; and colony 1 was inconclusive.
Figure 2. The surveyor assay indicated that Colony 3 and 6 were edited; colony 2 was not edited; and colony 1 was inconclusive.
Phase #3: Sequence Analysis of the Edited Colonies
- PCR products from Colonies 3 and 6 were further analyzed via Sanger Sequencing to determine the nature of the knockout (Figure 3).
- For colony 3 only one mutant sequence was detected, indicating that these cells are likely only heterozyotic knockouts. In colony 6 two different mutant sequences were detected.

Figure 3. For colony 3 only one mutant sequence was detected, indicating that these cells are likely only heterozyotic knockouts. In colony 6 two different mutant sequences were detected.
Phase #4: Second Round of Selection for Monoclonal Biallelic Knockout Clones
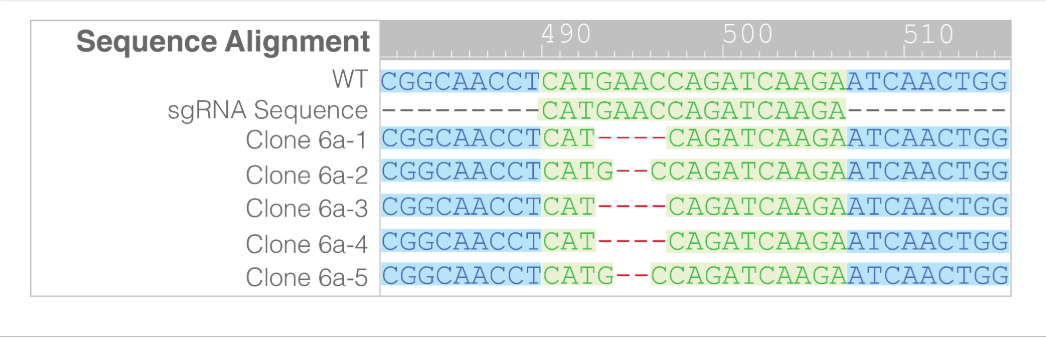
- Colony 6 was serial diluted into 96 well plates for monoclonal selection. Genomic DNA was extracted from these clones (i.e. 6a, 6b..), PCR amplified, cloned and sequenced.
- Of the colony 6 clones, sequencing showed that only clone 6a had a frameshift mutation in both alleles (Figure 4). A frameshift mutation disrupts the open reading frame, resulting in nonsense mediated decay of mRNA transcript.
Figure 4. Clones 6a, 6b and 6d all showed biallelic editing. Only clone 6a had frame shift mutations in both alleles. No WT sequences were detected in all subclones.
- Further sequencing of clone 6a confirmed that only two mutant alleles were present, the 2 bp and 4 bp deletions, and that no WT or other mutations were detected (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Further sequencing of 6a confirmed biallelic knock-out. No WT sequences were detected.
Phase #5: Confirmation of Knockout by Next Generation Amplicon Sequencing
- With next generation sequencing hundreds of thousands of alleles can be sequenced at once, resulting in a more robust dataset. By contrast Sanger sequencing is only feasible for 1-100 clones and therefore it can miss a large proportion of the population.
- Next generation sequencing was performed at each stage of selection to evaluate knockout (Figure 6). Before editing, only WT sequences were observed. After the first round of selection colony 6 showed a mixture of edited (70%) and WT (30%) sequences. Finally after monoclonal selection, clone 6a showed only edited sequences with no WT alleles present.
Figure 6. Next Generation Sequencing for CRISPR Knockout screening. A) Before knockout only WT sequences are detected. B) After Cas9 and sgRNA delivery, the first round of selection shows a mixed distribution of indel and WT sequences. C) After the second round of selection only knockouts remain.
Additional Information & MTA
FAQs
What should customers provide for this service?
Please supply the cells for this service. For frozen cells, please ship at least 2 vials (at least 106 each) on dry ice. An alternative method is to send us two T25 flask of live cells per sample, at 90% confluency. The flasks should be filled with complete medium without any air bubbles and at room temperature. Please ensure that the sterilization procedure is strictly observed. To avoid delays over the weekend, we recommend shipping the cells on a Monday or a Tuesday. Frozen cells are preferred over live cells. If your cell line already contains an antibiotic resistance marker, please specify. Our vectors have puromycin resistance by default. If your cells require medium other than DMEM and RPMI, we will also require 1L of the specified medium and any applicable growth factors or supplements to be provided by you for the project. Please submit all components of the complete media (e.g. if growth factors, cytokines etc. are applicable) individually to eliminate potential degradation of components in the media during transit. Kindly include instructions for making the complete media in your shipment. Additionally, please provide at least 5 x coated 6-well plates and 10 x T25 flasks if the cells require specially treated culture vessels. Once you have shipped your cells, please forward us the tracking number for custom clearance. Information on how to ship cell samples to abm can be found on our support page: https://www.abmgood.com/Technical-Support.html Please place an order first prior to submitting your samples. All samples received must have the order confirmation number indicated. Any samples received without this piece of information will be disposed off immediately upon receipt to ensure that all customer information is held in strict confidence.
Can this service be performed for canine derived cells?
Yes, we can use sgRNA targeting canine genome to make stable KO cell lines. Please provide the specific cell medium for canine cell culture.
Will CRISPR keep cutting the chromosome after the gene is edited?
CRISPR is sensitive to mismatches, so it is unlikely the CRISPR will keep cutting the chromosome after the gene is edited.
Is Nuclease or Nickase used? Can you use the double Nickase approach?
The approach used for the above service is sgRNA with Cas9 Nuclease, relying on NHEJ repair without a repair template. The Nickase approach is available but this will be at an additional charge and will be subject to a custom quotation as a different strategy will need to be devised.
How can you detect a mutation if there is no selection (by PCR using primers flanking the modified site or the T7 endonuclease I assay)?
Yes, that is one method used. Other methods include Sanger sequencing, and Western Blot if the antibody is provided by the customer.
How many sgRNAs are designed and synthesized for this service? Are pooled sgRNAs used?
We design 3 sgRNAs at the time of order placement, however only 1 sgRNA is used to achieve knockout. In the case that the first sgRNA does not allow for success, we would try another from the set of 3 synthesized sgRNAs.
Can you offer off-target site prediction service and off-target site analysis service (Sanger sequence)?
When we design the sgRNAs, the design software will predict the number of off-targets, which is usually 0 for the sgRNAs that we select. Off-target analysis: This will need to be done by NGS, whole genome sequencing or exome sequencing, which would require comparing the control (before) sample to the genome edited sample (after). If this is a desired option, we can provide a quote for it, but it will likely be at least $2200 for analyzing 1-2 clones by Exome Seq, and higher for whole genome sequencing.
How is KO confirmed?
Citations
| 01 |
Kang, Y. J. et al. “Regulation of NKT cell-mediated immune responses to tumours and liver inflammation by mitochondrial PGAM5-Drp1 signalling.” Nat. Commun. (2015) 6:8371 doi: 10.1038/ncomms9371
|
| 02 |
Jiang, G. et al. “Isorhapontigenin (ISO) inhibits invasive bladder cancer (BC) formation in vivo and human BC invasion in vitro by targeting STAT1/FOXO1 Axis.” Cancer Prev Res. Published Online First April 14, 2016.doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-15-0338
|
| 03 | Okugawa, Y. et al. “Clinical significance of SNORA42 as an oncogene and a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer.” Gut (2015)doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309359 |